$1,990.00 – $2,490.00
Haydn N. Allbutt and Jasmine M. Henderson employed the Narrow Beam Apparatus in their research involving the rat model of Parkinson’s disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine. This test evaluates a rat’s ability to traverse a narrow, elevated beam made of wood or similar material.
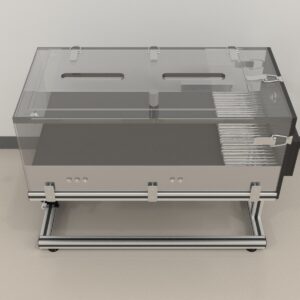
In the current experiments, a long acrylic beam was utilized. This beam was supported by acrylic brackets at both ends, with a vertical drop at the “starting” end and a platform at the opposite end. Adjacent to the platform was the home cage of the rat being tested. To ensure safety, a 1-meter-wide foam pad was placed beneath the beam to cushion any falls and prevent injury.
MazeEngineers provides the Narrow Beam Apparatus.

MazeEngineers offers custom-built behavioral mazes at no extra cost—designed to fit your exact research needs. Eliminate reproducibility issues from poor sizing or lingering scent cues with precision-engineered, modular, and smart mazes that adapt in real time to animal behavior. Publish new protocols, run adaptive experiments, and push the boundaries of behavioral science.


Mouse Features | |
Length of beam: 69.3cm | |
Width of beam: 2.6cm | |
Height of beam: 2cm | |
Distance of beam from the ground with supports: 53cm | |
Width of foam padding: 0.6m | |
Thickness of foam padding: 7.9cm |
Rat Features | |
Length of beam: 105cm | |
Width of beam: 4cm | |
Height of beam: 3 cm | |
Distance of beam from the ground with supports: 80cm | |
Width of foam padding: 1m | |
Thickness of foam padding: 12cm |
The Narrow Beam Apparatus is a behavioral task used to assess motor balance and coordination in rodents. In rodents, genetic manipulations, brain injury, and pharmacological treatments may alter motor skills (Luong et al., 2011).
The Narrow Beam Apparatus is designed to assess motor balance and coordination in rodents. The apparatus consists of an elevated beam with a starting area and an exit platform. The subject crosses the beam by utilizing its natural ability to show aversion to open and exposed places. The home cage placed beside the exit platform acts as a motivating factor for the subject to cross the beam. (Doaee et al., 2019). The Narrow Beam task is easy to perform and requires minimum time to perform the task. The Narrow Beam Apparatus can be effectively used to evaluate the role of different pharmaceutical drugs, toxins on the motor dysfunction of Parkinson’s disease rodent models (Doaee et al., 2019; Luong et al., 2011). It can also be used to assess the role of physical training and the role of circadian rhythms on the motor control of rodents. (Allbutt & Henderson, 2007; Cao & Rodgers,1998).
Other apparatuses to understand motor balance and coordination in rodents include the Linear Maze, the Gait test, and the Parallel Bars.
and 3 cm in depth. Supported at each end, the beam is elevated 80 cm above the ground. A starting line is marked 20 cm from the edge of the beam to designate the beginning of the trial. At the opposite end of the beam, there is a platform that can be linked to the subject’s home cage. To protect against injuries from falls, a 1 cm thick foam padding, extending 12 cm in width, is placed beneath the beam.
Ensure the apparatus is thoroughly cleaned before each trial to prevent any residual stimuli from affecting the results. Make sure the testing area is well-lit. For enhanced observation, consider using the Noldus EthoVision XT system.
The Narrow Beam Task
Position the subject’s home cage at the platform end of the Narrow Beam Apparatus. Place the subject at the starting area, ensuring it faces the home cage. Begin the trial by releasing the subject and starting the timer. The subject should cross the start line within one minute. Stop the timer as soon as the subject fully reaches the exit platform and conclude the trial. The entire task should be completed within a maximum of 2 minutes. Return the subject to its home cage and perform a total of five trials.
In their 2007 study, Allbutt and Henderson explored how training, timing, and Parkinson’s disease influence motor control in rodents. The subjects were categorized into three groups: Group 1 (n=8) and Group 2 (n=20), both unoperated, and Group 3 (n=20), which included ten rodents with 6-OHDA injections and ten with saline sham injections. To assess the impact of training, subjects ran on the Narrow Beam Apparatus 12 times over 23 days, typically between 4-5 pm. The influence of testing time was also evaluated, with subjects running during various time windows such as 4:30-5 pm and 5:10-6:20.
Group 3, consisting of lesioned rodents, was specifically tested on the Narrow Beam. The study found that subjects quickly adapted to the Narrow Beam Task after just one training session, and the time to cross the beam remained consistent with experience. However, the latency to start the task increased with more frequent trials (p<0.05). The time of day did not affect either the latency to begin the task or the total time to cross the beam. Notably, 6-OHDA-injected rodents exhibited a four-fold increase in both latency and total time to complete the task. The study concluded that the Narrow Beam Apparatus is a valuable tool for examining motor dysfunction in rodent models of Parkinson’s disease.
Doaee et al. (2019) examined the effects of Boswellia serrata oleo-gum resin on motor dysfunction in a 6-OHDA rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. The study included three groups: a sham group, a lesion group (6-OHDA), and a three-lesion group. Each group received a treatment of ethyl alcoholic extract of B. serrata at doses of 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg, respectively, over a period of three weeks. Motor behavior was evaluated using rotational and Narrow Beam tasks. Additionally, oxidative stress markers were measured in the striatal and midbrain homogenates.
The results indicated a significant increase in contralateral rotations in the 6-OHDA group compared to the sham group (p<0.001). Treatment with B. serrata resin extract at doses of 125 mg/kg and 250 mg/kg led to a reduction in rotations compared to the 6-OHDA group (p<0.001 for both doses). The Narrow Beam Task results showed that the 6-OHDA group had a marked increase in both latency to cross the start line (p<0.001) and total time taken (p<0.001).
Additionally, treatment with B. serrata extract at doses of 125, 250, and 500 mg/kg led to reductions in both latency and total time (p<0.001, p<0.001, and p<0.01, respectively). Biochemical analysis showed no significant differences in oxidative stress marker levels across the groups. The findings suggest that B. serrata resin extract functions as both an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent, contributing to improvements in motor deficits associated with Parkinson’s Disease.
The Narrow Beam Apparatus is straightforward and quick to assemble. Conducting the task is simple and does not necessitate prior training for the subjects, allowing for efficient task execution. This apparatus is well-suited for assessing the impact of different drugs, pharmacological agents, and toxins on motor balance in rodent models.
Inadequate handling of the subjects can induce stress, potentially affecting their behavior. Surrounding visual, olfactory, or auditory stimuli might influence the results of observations. Additionally, factors such as the rodent’s age, strain, and species can impact the findings.
| Species | Mouse, Rat |
|---|
There are no questions yet. Be the first to ask a question about this product.
Monday – Friday
9 AM – 5 PM EST
DISCLAIMER: ConductScience and affiliate products are NOT designed for human consumption, testing, or clinical utilization. They are designed for pre-clinical utilization only. Customers purchasing apparatus for the purposes of scientific research or veterinary care affirm adherence to applicable regulatory bodies for the country in which their research or care is conducted.